Saber is one of the most common -ER verbs in Spanish. Since it refers to knowledge, this verb is applied in daily conversations. Because it has many irregularities, we’ll go over the key saber conjugation charts in this guide. Here’s is what you’ll learn:
- Saber Overview
- Indicative Tenses of Saber Conjugations
- Subjunctive Tenses of Saber Conjugations
- Imperative (Commands) of Saber Conjugations
- Uses & Examples
- Download Saber Conjugation Tables & Uses Cheat sheets
- Saber Conjugation Practice Quiz
In Spanish, the verb saber has different applications. The conjugation charts below only have one translation to keep the tables as organized as possible. You can learn more about the meanings of ‘saber’ in the section Uses & Meanings.
Overview of Saber
| Verb Characteristic | Property |
|---|---|
| Verb Type | -ER |
| Irregular | Yes |
| Infinitive | Saber |
| Gerund (Present Participle) Form | Sabiendo |
| Past Participle Form | Sabido |
| Synonyms | Conocer, entender, comprender. |
Irregularities:
- Present: sé only ‘yo’.
- Preterite: sup for all subject pronouns.
- Future & Conditional: sabr for all subject pronouns.
- Present subjunctive: sep for all subject pronouns.
- Imperfect Subjunctive: supie for all subject pronouns.
- Affirmative imperative: sep for ‘usted’ and ‘ustedes’.
- Negative imperative: sep for all subject pronouns.
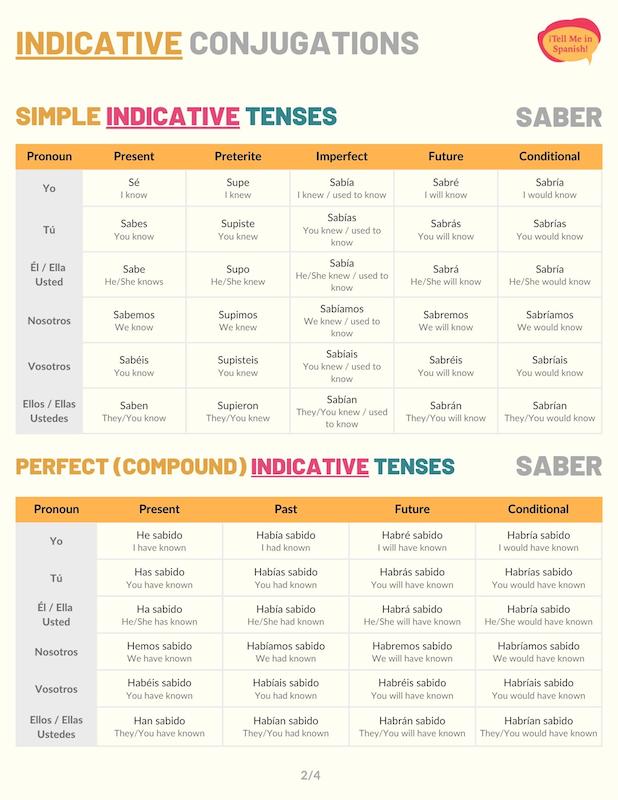
Indicative Conjugations of Saber
Present tense
Saber conjugations in the present tense are mostly regular, except for the pronoun ‘yo’. You can check these changes in the conjugation chart below. The present tense conjugations of saber are used to talk about things people currently know. For example: No sé quién es ella.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Sé | I know |
| Tú | Sabes | You know |
| Él / Ella Usted | Sabe | He/She knows You (formal) know |
| Nosotros | Sabemos | We know |
| Vosotros | Sabéis | You know |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Saben | They know You (plural) know |
Preterite tense
The preterite tense conjugations of saber are irregular. We use the stem sup to conjugate to this tense. Additionally, some subject pronouns use unaccented -AR endings, while others use unaccented -ER endings. You can see these patterns in the preterite conjugation chart below.
Conjugate saber to the preterite tense to talk about what people knew or found out at some point. For example: ¿Cómo supieron que era yo?
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Supe | I knew |
| Tú | Supiste | You knew |
| Él / Ella Usted | Supo | He/She knew You (formal) knew |
| Nosotros | Supimos | We knew |
| Vosotros | Supisteis | You knew |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Supieron | They knew You (plural) knew |
Imperfect tense
In the imperfect indicative tense, saber is a regular verb. Use this verb’s imperfect conjugations to refer to the things people knew or didn’t know for an extended period of time in the past. Here is an example: Ella no sabía cómo cocinar.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Sabía | I knew I used to know |
| Tú | Sabías | You knew You used to know |
| Él / Ella Usted | Sabía | He/She knew He/She used to know You (formal) knew You (formal) used to know |
| Nosotros | Sabíamos | We knew We used to know |
| Vosotros | Sabíais | You knew You used to know |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Sabían | They knew They used to know You (plural) knew You (plural) used to know |
Near future
To conjugate saber to the Spanish near or immediate future, use the formula ir (present tense) + a + saber. With this tense, saber expresses that a person is going to know something soon in the future. En unas horas, vamos a saber qué pasó.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Voy a saber | I’m going to know |
| Tú | Vas a saber | You’re going to know |
| Él / Ella Usted | Va a saber | He/She is going to know You (formal) are going to know |
| Nosotros | Vamos a saber | We’re going to know |
| Vosotros | Vais a saber | You’re going to know |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Van a saber | They’re going to know You (plural) are going to know |
Future simple tense
Saber future conjugations are formed with the stem sabr. Conjugate saber to the future simple tense to convey that someone will know or find out something at some moment in the future. For example: Si no nos ayudas, nunca sabremos qué pasó.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Sabré | I will know |
| Tú | Sabrás | You will know |
| Él / Ella Usted | Sabrá | He/She will know You (formal) will know |
| Nosotros | Sabremos | We will know |
| Vosotros | Sabréis | You (formal) will know |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Sabrán | They will know You (plural) will know |
Conditional tense
The Spanish conditional tense of ‘saber’ is also formed with the stem sabr. Use these conjugations to talk about what people would know. For instance: Sin su celular, ellos no sabrían cómo llegar al museo.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Sabría | I would know |
| Tú | Sabrías | You would know |
| Él / Ella Usted | Sabría | He/She would know You (formal) would know |
| Nosotros | Sabríamos | We would know |
| Vosotros | Sabríais | You would know |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Sabrían | They would know You (plural) would know |
Present perfect tense
In Spanish, the indicative present perfect tense is formed with structure haber in the present tense + sabido (past participle). We use these saber conjugations to refer to what people have or haven’t known. For instance: No hemos sabido nada de Mateo.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | He sabido | I have known |
| Tú | Has sabido | You have known |
| Él / Ella Usted | Ha sabido | He/She has known You (formal) have known |
| Nosotros | Hemos sabido | We have known |
| Vosotros | Habéis sabido | You have known |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Han sabido | They have known You (plural) have known |
Past perfect
Saber conjugated to the past perfect tense in Spanish communicates that someone had or hadn’t known something before another past action or past time frame. For example: Hasta hoy, no habíamos sabido nada de español.
To form this tense, use haber (imperfect form) + past participle form of ‘saber’.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Había sabido | I had known |
| Tú | Habías sabido | You had known |
| Él / Ella Usted | Había sabido | He/She had known You (formal) had known |
| Nosotros | Habíamos sabido | We had known |
| Vosotros | Habíais sabido | You had known |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habían sabido | They had known You (plural) had known |
Future perfect
In the future perfect tense, saber communicates that people will have known or found something out by or before a certain moment in the future. These conjugations are also used to talk about what someone might have known. Dentro de poco, habremos sabido si esto funcionó.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Habré sabido | I will have known |
| Tú | Habrás sabido | You will have known |
| Él / Ella Usted | Habrá sabido | He/She will have known You (formal) will have known |
| Nosotros | Habremos sabido | We will have known |
| Vosotros | Habréis sabido | You will have known |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habrán sabido | They will have known You (plural) will have known |
Conditional perfect
When conjugated to the conditional perfect tense, saber communicates that someone would have known something as long as a past condition had been met. For instance: Si hubieras puesto atención, habrías sabido que mañana no hay clases.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Habría sabido | I would have known |
| Tú | Habrías sabido | You would have known |
| Él / Ella Usted | Habría sabido | He/She would have known You (formal) would have known |
| Nosotros | Habríamos sabido | We would have known |
| Vosotros | Habríais sabido | You would have known |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habrían sabido | They would have known You (plural) would have known |
Progressive tenses
Estar conjugated + sabiendo (present participle) is the formula to form the Spanish progressive tenses. Because saber refers to the knowledge someone has, had or will have, these forms are not common since they emphasize that someone is knowing something at the moment of speaking.
Saber Subjunctive Conjugations
The subjunctive mood in Spanish is used to talk about wishes, requests, suggestions, expectations, doubts, or hypothetical situations. Below are the saber conjugation charts for the subjunctive tenses you need to know to become fluent in contemporary Spanish.
Present subjunctive
Saber subjunctive conjugations are formed with the stem sep. We use saber’s subjunctive forms to hope or request that someone knows certain things or how to do something. For example: Espero que mañana sepas arreglar esto.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Sepa | I know |
| Tú | Sepas | You know |
| Él / Ella Usted | Sepa | He/She knows You (formal) know |
| Nosotros | Sepamos | We know |
| Vosotros | Sepáis | You know |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Sepan | They know You (plural) know |
Present perfect subjunctive
Haber in the present subjunctive + sabido (Spanish past participle form) is the formula to conjugate ‘saber’ to the present perfect subjunctive. With this tense, this verb is used to wonder, express doubt, or wish that a person has already known something. For instance: Dudo que Celia haya sabido algo.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Haya sabido | I have known |
| Tú | Hayas sabido | You have known |
| Él / Ella Usted | Haya sabido | He/She has known You (formal) have known |
| Nosotros | Hayamos sabido | We have known |
| Vosotros | Hayáis sabido | You have known |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Hayan sabido | They have known You (plural) have known |
Imperfect subjunctive
Supie is the stem we use to conjugate saber to the imperfect subjunctive tense. In this tense, saber is used to talk about past suggestions, requests, and wishes someone had about a person knowing something. Ojalá supiéramos preparar pasteles.
The imperfect subjunctive has two conjugation models depending on the type of Spanish you use:
Latin American Spanish version
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Supiera | I knew |
| Tú | Supieras | You knew |
| Él / Ella Usted | Supiera | He/She knew You (formal) knew |
| Nosotros | Supiéramos | We knew |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Supieran | They knew You (plural) knew |
Note: Since vosotros is not used in Latin American Spanish, the conjugation chart above doesn’t include the saber conjugation for this pronoun.
Castilian Spanish version
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Supiese | I knew |
| Tú | Supieses | You knew |
| Él / Ella Usted | Supiese | He/She knew You (formal) knew |
| Nosotros | Supiésemos | We knew |
| Vosotros | Supieseis | You knew |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Supiesen | They knew You (plural) knew |
Past perfect subjunctive
The past perfect subjunctive of saber communicates that someone would have known something if a past circumstance had occurred. Additionally, these conjugations also express regret for knowing or not knowing something.
For example: Si hubiera sabido que no te gusta el pescado, habría cocinado otra cosa.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Hubiera sabido | I had known |
| Tú | Hubieras sabido | You had known |
| Él / Ella Usted | Hubiera sabido | He/She had known You (formal) had known |
| Nosotros | Hubiéramos sabido | We had known |
| Vosotros | Hubierais sabido | You had known |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Hubieran sabido | They had known You (plural) had known |
Saber Imperative Conjugations
The Spanish imperative mood allows you to command people to do or not do something.
Affirmative commands
Saber affirmative commands are irregular only for ‘usted’ and ‘ustedes’. These commands allow you to order people to know something, as a result, they’re only used in very few situations. For example: Sepan que hice lo que pude.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Tú | Sabe | Know |
| Usted | Sepa | Know |
| Vosotros | Sabed | Know |
| Ustedes | Sepan | Know |
Negative commands
Because you cannot command people not to know something, the negative imperative forms of saber are never used in Spanish.
Meanings of Saber & Examples
Since you already know how to conjugate saber in Spanish, here are some examples of how to use this verb.
- Talking about things you know or found out
Saber + infinitive verb refers to the things you know how to do. However, you can also use nouns to talk about things you know.
[Saber conjugated] + [complement]
Supimos que te casaste. ¡Felicidades!
We heard that you got married. Congratulations!
Ellos no sabían que hoy es tu cumpleaños.
They didn’t know that today is your birthday.
Ya sabemos conjugar el verbo saber.
We already know how to conjugate the verb saber.
Take Note: Even though saber and conocer seem like synonyms, they’re not always used interchangeably. In this article, you can learn the difference between saber and conocer.
- Describing something’s taste
[Saber] + (adjective)
¿Cómo sabe la sopa?
How does the soup taste?
Las galletas sabían riquísimas.
The cookies tasted great.
Take Note: When describing the flavor of something, you can use the noun ‘sabor’ as the literal translation of ‘flavor’ in Spanish. Notice that the only difference between this noun and the verb ‘saber’ is the -er and -or endings.
Download Saber Conjugation Charts & Uses Cheat sheets
Saber is an irregular verb and it can be very challenging for Spanish beginners to learn how to conjugate this verb with all of its different forms. I’ve created a downloadable PDF with all of the saber conjugation tables as well as its uses, meanings, and real-world examples so you can keep it with you and study at your own pace.
Practice Quiz: Saber Conjugation

Now that you’ve learned how to conjugate saber in Spanish, you can take the saber conjugation practice quiz to drill this verb in all of its tenses as an fun, interactive way to memorize all of its irregularities.



