When it comes to Spanish verbs, seguir conjugation patterns are great to practice the -IR conjugation group and E to I stem-changing verbs. Because this is also a common verb you’ll use in your conversations, in this guide, we’ll learn how to conjugate seguir.
Here is what we’ll cover:
- Seguir Overview
- Indicative Tenses of Seguir Conjugations
- Subjunctive Tenses of Seguir Conjugations
- Imperative (Commands) of Seguir Conjugations
- Uses & Examples
- Download Seguir Conjugation Tables & Uses Cheat sheets
- Seguir Conjugation Practice Quiz
Overview of Seguir
| Verb Characteristic | Property |
|---|---|
| Verb Type | -IR |
| Irregular | No |
| Infinitive | Seguir |
| Gerund (Present Participle) Form | Siguiendo |
| Past Participle Form | Seguido |
| Synonyms | Perseguir, continuar, acosar. |
Stem Changes: E to IE
- Present indicative: sig for ‘yo’ and sigu for ‘tú’, ‘él/ella’, ‘usted’ and their plural forms.
- Preterite: sigu for the third person singular and plural.
- Present subjunctive: sig for all subject pronouns.
- Imperfect subjuntive: siguie for all subject pronouns.
- Affirmative commands: sigu for ‘tú’, sig for ‘usted’, and ‘ustedes’.
- Negative commands: sig for all subject pronouns.
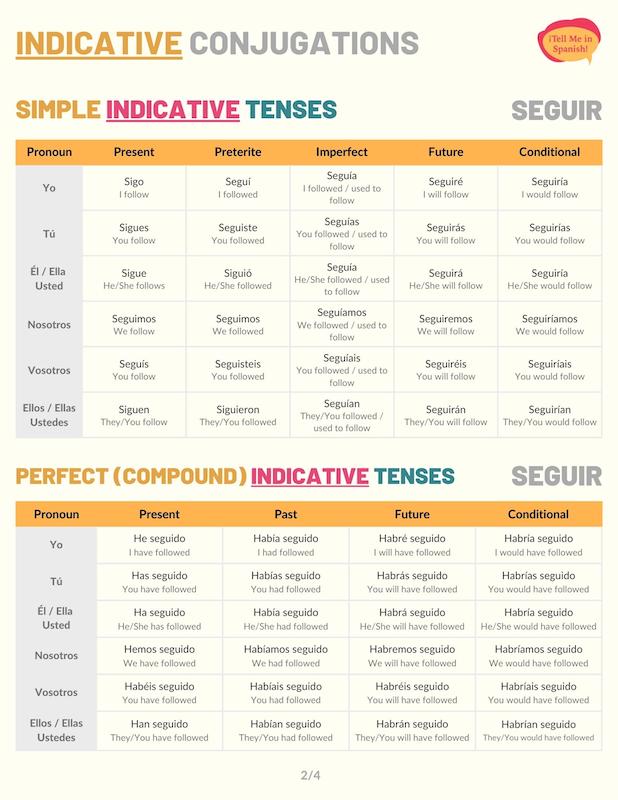
Indicative Conjugations of Seguir
Present tense
Seguir present tense conjugation is formed with an E to I stem change. However, this change is not applied to ‘nosotros’ and ‘vosotros’. Conjugate seguir to the present tense to express that someone is currently following a topic, a person, or still doing something.
For example: Nosotros seguimos a mi mamá.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Sigo | I follow |
| Tú | Sigues | You follow |
| Él / Ella Usted | Sigue | He/She follows You (formal) follow |
| Nosotros | Seguimos | We follow |
| Vosotros | Seguís | You follow |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Siguen | They follow You (plural) follow |
Take Note: The letter g in Spanish has different sounds depending on the vowel which follows it. Notice that, in its infinitive form, seguir has a soft g sound. Since this is the sound we must keep, we must add a ‘u’ in certain conjugations to avoid having a hard g sound.
Preterite tense
Seguir preterite conjugation has an E to I stem change only for the third person singular and plural. Use the preterite tense forms to communicate that someone followed something or another person in the past. El perro me siguió hasta mi casa.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Seguí | I followed |
| Tú | Seguiste | You followed |
| Él / Ella Usted | Siguió | He/She followed You (formal) followed |
| Nosotros | Seguimos | We followed |
| Vosotros | Seguisteis | You followed |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Siguieron | They followed You (plural) followed |
Imperfect tense
When conjugated to the imperfect indicative tense, seguir has no stem changes. We use these conjugations to explain that someone used to follow a topic or a person for a long period of time in the past. For example: Cuando era un cachorro, ese perro siempre nos seguía.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Seguía | I followed I used to follow |
| Tú | Seguías | You followed You used to follow |
| Él / Ella Usted | Seguía | He/She followed He/She used to follow You (formal) followed You (formal) used to follow |
| Nosotros | Seguíamos | We followed We used to follow |
| Vosotros | Seguíais | You followed You used to follow |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Seguían | They followed They used to follow You (plural) followed You (plural) used to follow |
Near future
Seguir conjugated to the near future expresses that a person will follow something or someone soon in the future. To form this tense, use the structure ir (present tense) + a + infinitive verb (seguir, in this case). Here is an example: Voy a seguir a este influencer.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Voy a seguir | I’m going to follow |
| Tú | Vas a seguir | You’re going to follow |
| Él / Ella Usted | Va a seguir | He/She is going to follow You (formal) are going to follow |
| Nosotros | Vamos a seguir | We’re going to follow |
| Vosotros | Vais a seguir | You’re going to follow |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Van a seguir | They’re going to follow You (plural) are going to follow |
Future simple tense
Use seguir in the future tense form to convey that someone will follow something or another person at some point in the future. With these conjugations, you can also use seguir to talk about the things you’ll keep doing in the future. For example: Todavía seguiré viviendo aquí.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Seguiré | I will follow |
| Tú | Seguirás | You will follow |
| Él / Ella Usted | Seguirá | He/She will follow You (formal) will follow |
| Nosotros | Seguiremos | We will follow |
| Vosotros | Seguiréis | You (formal) will follow |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Seguirán | They will follow You (plural) will follow |
Conditional tense
In the Spanish conditional tense, seguir expresses that people would follow someone or a topic if some circumstances were met. You can also use these forms to hypothesize why people would follow something.
For example: ¿Por qué me seguiría ese muchacho?
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Seguiría | I would follow |
| Tú | Seguirías | You would follow |
| Él / Ella Usted | Seguiría | He/She would follow You (formal) would follow |
| Nosotros | Seguiríamos | We would follow |
| Vosotros | Seguiríais | You would follow |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Seguirían | They would follow You (plural) would follow |
Present perfect tense
In Spanish, the present perfect tense is formed with haber in the present tense + seguido (past participle). Use these seguir conjugations to talk about what someone has or hasn’t followed. Chicas, ¿habéis seguido las instrucciones?
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | He seguido | I have followed |
| Tú | Has seguido | You have followed |
| Él / Ella Usted | Ha seguido | He/She has followed You (formal) have followed |
| Nosotros | Hemos seguido | We have followed |
| Vosotros | Habéis seguido | You have followed |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Han seguido | They have followed You (plural) have followed |
Past perfect
The past perfect conjugations of seguir communicate that someone had followed something or someone before some other reference point in the past. Juan me había seguido todo el día. To form the past perfect, use the imperfect form of ‘haber’ and the past participle form of ‘seguir’.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Había seguido | I had followed |
| Tú | Habías seguido | You had followed |
| Él / Ella Usted | Había seguido | He/She had followed You (formal) had followed |
| Nosotros | Habíamos seguido | We had followed |
| Vosotros | Habíais seguido | You had followed |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habían seguido | They had followed You (plural) had followed |
Future perfect
Seguir conjugated to the Spanish future perfect conveys that someone will have followed something by or before a certain moment in the future. We also use these forms to talk about what someone might follow. For example: ¿Por qué te habrán seguido?
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Habré seguido | I will have followed |
| Tú | Habrás seguido | You will have followed |
| Él / Ella Usted | Habrá seguido | He/She will have followed You (formal) will have followed |
| Nosotros | Habremos seguido | We will have followed |
| Vosotros | Habréis seguido | You will have followed |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habrán seguido | They will have followed You (plural) will have followed |
Conditional perfect
In Spanish, we use seguir conditional perfect conjugations to express that someone would have followed something if a past action had been completed. You can also use these forms to hypothesize why a person followed something.
For example: Si no hubiera traído carne, el perro no me habría seguido.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Habría seguido | I would have followed |
| Tú | Habrías seguido | You would have followed |
| Él / Ella Usted | Habría seguido | He/She would have followed You (formal) would have followed |
| Nosotros | Habríamos seguido | We would have followed |
| Vosotros | Habríais seguido | You would have followed |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habrían seguido | They would have followed You (plural) would have followed |
Progressive tenses
The progressive tenses of seguir convey that someone is following something at the moment of speaking. These tenses are formed with estar conjugated + present participle (siguiendo). Here is an example: Ese chico te estuvo siguiendo todo el día.
| Progressive Tense | Formula | Translation Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present | Estar (present) + siguiendo | I am following |
| Preterite | Estar (preterite) + siguiendo | You were following |
| Imperfect | Estar (imperfect) + siguiendo | He was following |
| Future | Estar (future) + siguiendo | We will be following |
| Conditional | Estar (conditional) + siguiendo | They would be following |
Take Note: The present participle form of seguir also has E to I stem changes. Click here to check other verbs that follow this same pattern.
Seguir Subjunctive Conjugations
The subjunctive mood in Spanish conveys uncertainty, wishes, suggestions, requests, expectations and refers to hypothetical situations. In the sections below, you’ll find all of the seguir conjugation charts. In these tenses, seguir is also an E to I stem-changing verb.
Present subjunctive
All seguir subjunctive conjugations use the stem sig. This spelling change is done to keep pronunciation consistent. Conjugate seguir to the present subjunctive to request or wish that someone follows something. For example: Niños, no quiero que me sigan.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Siga | I follow |
| Tú | Sigas | You follow |
| Él / Ella Usted | Siga | He/She follows You (formal) follow |
| Nosotros | Sigamos | We follow |
| Vosotros | Sigáis | You follow |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Sigan | They follow You (plural) follow |
Present perfect subjunctive
Haber in the present subjunctive + seguido is how you form the present perfect subjunctive of ‘seguir’. We use these conjugations to wonder or wish that someone has already followed something. No creo que hayan seguido las instrucciones.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Haya seguido | I have followed |
| Tú | Hayas seguido | You have followed |
| Él / Ella Usted | Haya seguido | He/She has followed You (formal) have followed |
| Nosotros | Hayamos seguido | We have followed |
| Vosotros | Hayáis seguido | You have followed |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Hayan seguido | They have followed You (plural) have followed |
Imperfect subjunctive
All the Spanish imperfect subjunctive forms of ‘seguir’ have an E to I stem change. We use these conjugations to talk about past suggestions, requests, wishes, or expectations you had about someone following something. Te dije que siguieras las instrucciones.
Depending on the type of Spanish you use, there are two conjugation models for the imperfect subjunctive:
Latin American Spanish version
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Siguiera | I followed |
| Tú | Siguieras | You followed |
| Él / Ella Usted | Siguiera | He/She followed You (formal) followed |
| Nosotros | Siguiéramos | We followed |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Siguieran | They followed You (plural) followed |
Note: Latin American Spanish speakers don’t use the pronoun ‘vosotros’. As a result, that conjugation has been omitted in the above conjugation table.
Castilian Spanish version
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Siguiese | I followed |
| Tú | Siguieses | You followed |
| Él / Ella Usted | Siguiese | He/She followed You (formal) followed |
| Nosotros | Siguiésemos | We followed |
| Vosotros | Siguieseis | You followed |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Siguiesen | They followed You (plural) followed |
Past perfect subjunctive
Seguir conjugated to past perfect subjunctive expresses that someone would have followed something if a past condition was completed. These forms can also express regret or hypothetical results if someone had followed something.
For example: Si me hubieras seguido, no te habrías perdido.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Hubiera seguido | I had followed |
| Tú | Hubieras seguido | You had followed |
| Él / Ella Usted | Hubiera seguido | He/She had followed You (formal) had followed |
| Nosotros | Hubiéramos seguido | We had followed |
| Vosotros | Hubierais seguido | You had followed |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Hubieran seguido | They had followed You (plural) had followed |
Seguir Imperative Conjugations
In Spanish, we use imperative conjugations to order someone to do or not to do something.
Affirmative commands
Seguir affirmative commands conjugations are formed with the stem sig for all subject pronouns except ‘vosotros’. Notice that you must also add a ‘u’ to the form ‘tú’. Use the affirmative imperative of ‘seguir’ to order people to follow something. ¡Siga ese carro!
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Tú | Sigue | Follow |
| Usted | Siga | Follow |
| Vosotros | Seguid | Follow |
| Ustedes | Sigan | Follow |
Negative commands
To order people not to follow something, use the negative imperative of ‘seguir’. As shown in the conjugation chart below, these forms also follow an E to I stem change. Here is a sentence: No me sigas.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Tú | No sigas | Don’t follow |
| Usted | No siga | Don’t follow |
| Vosotros | No sigáis | Don’t follow |
| Ustedes | No sigan | Don’t follow |
Meanings of Seguir & Examples
Now that we’ve learned how to conjugate seguir in Spanish, here are some formulas and examples of how to use this verb.
1. Talk about following something or someone
[Seguir conjugated] + [complement]
Chicos, ¿siguieron las indicaciones?
Guys, did you follow the instructions?
No sabía que me siguieras en Instagram.
I didn’t know that you followed me on Instagram.
Take Note: You can use Spanish direct object pronouns to replace the thing or person you’re following.
2. Expressing someone still does something
[Seguir conjugated] + [past or present participle]
¿Todavía siguen enojados conmigo?
Are you still mad at me?
Por ahora, seguiré viviendo aquí.
For the time being, I will continue living here.
Take Note: Spanish past participles are used to build perfect tenses or as adjectives (like the above example). Do not confuse them with present participles. Present participles in Spanish refer to ongoing or continuous actions.
Download Seguir Conjugation Charts & Uses Cheat sheets
Stem-changing verbs like seguir can be difficult to commit to memory and learn by heart. I’ve created this cheat sheets PDF you can download with all of the seguir conjugation charts along with its meanings and uses for you to review later when you need it.
Practice Quiz: Seguir Conjugation

Now that you’ve learned how to conjugate seguir in Spanish, you can put your skills to the test by practicing all of its regular and stem-changing forms with the seguir conjugation practice quiz.



